Capabilities and Tools
Air Quality Testing Laboratory
The Air Quality Testing Laboratory is a unique research facility for the development and validation of innovative air quality technologies.
The facility offers access to bench-scale experiments, room-sized chambers and a broad range of analytical facilities to:
- Develop and test air cleaning technologies (active and passive).
- Characterize building materials for pollutant and moisture control.
- Optimize HVAC, ventilation and range hood technologies.
- Evaluate exposure and health effects in occupants.

This Indoor Air Quality (IAQ) Scientific Findings Resource Bank (IAQ-SFRB) serves as a resource for public health professionals, building professionals, and others who seek scientific information about the effects of IAQ on people's health or work performance. It provides information summarizing the state of scientific knowledge about the relationships between people's health and productivity and the IAQ conditions or associated building characteristics in which the people work or reside. The summaries also include brief descriptions of the actions that may be taken to improve the pertinent aspects of IAQ, including those related to building design, construction, operation, maintenance, and occupant activities.
Kitchen Range Hood Capture Efficiency Testing
Capture efficiency is the percentage of pollutants emitted at the cooking surface that are captured by the exhaust hood. Our facility enables measurement of capture efficiency, sound level, and airflow for wall-mounted, island and downdraft exhaust systems. We can adjust how the range hood is installed, and measure pollutant capture efficiency using idealized emitters or during realistic cooking conditions using gas or electric fuel. We can simultaneously measure pollutant concentrations, such as as carbon monoxide, nitrogen oxides, formaldehyde, and fine particulates generated during cooking.
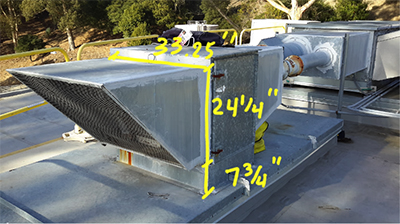 RTU Outdoor Airflow Testing
RTU Outdoor Airflow Testing
This unique test system for characterizing the accuracy of outdoor air measurement technologies (OAMTs) is located on the roof of a Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory building. The evaluation system has a maximum flow rate of approximately 1,000 L s-1 (2100 cfm, or 2.7 m s-1 with a 24”x24” inlet), typical of a rooftop unit with 20kW (6 ton) of refrigeration capacity. A roof top location is desirable because wind speed and direction can affect the accuracy of an OAMT. In periods with precipitation or fog, small suspended water droplets may be carried into the RTU by the OA, possibly affecting measurement accuracy. The airflow rates indicated by the OAMTs are compared to airflow rates determined using downstream highly accurate nozzle flow meters (Thermo-Brandt Instruments) with upstream honeycomb airflow straighteners, connected to research-grade pressure transducers (Energy Conservatory APT).

Population Impact Assessment Modeling Framework
The Population Impact Assessment Modeling (PIAM) Framework approach applies physics-based simulation model(s) to calculate one or more environmental or energy performance parameters for each home in a sample cohort selected or developed to represent a population. Results from the individual homes are compiled to provide the statistics for population impacts. The approach can be applied at varying temporal or spatial scales. PIAMF is currently used to address specific questions on energy use and indoor air quality in homes.

